Generative AI and Sustainability
While most of the world is swept up by the Generative Artificial Intelligence (GAI) storm, another school is considering the energy use and savings of such GAI use.
Consider the energy use table below between ChatGPT and Google Search
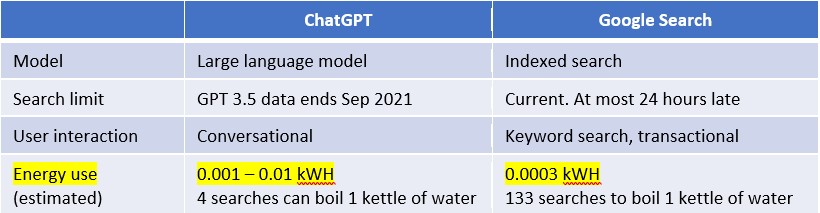
The use of ChatGPT is 3 to 30 times more energy intensive than Google Search.
Use of GAI to create energy saving solutions
One most obvious method to save energy is to ask GAI how it can do so. But GAI is not a search engine. It has a cut-off date to its training so it may not be the more up-to-date even with its own developments! I asked Gemini and it told me to do a search to be up-to-date.
Research is underway to adapt various GAI models and algorithms to for energy use reduction. Here is a paper that discusses the various GAI models that can be used to reduce carbon emissions in networks, cloud and centralized computing.
Using GAI more efficiently
Training a whole new Large Language model is resource-intensive and time-consuming. If you are only adding company- or product-specific information to your chatbot, you may be able to get away with fine-tuning your LLM or by using Retrieval-augmented Generation (RAG). You can augment with a webpage or PDF articles or a customer support database extracted into JSON files. Both methods mean you can start with a smaller LLM model and save time and GPU resources. RAG and fine-tuning are also very effective for data that is constantly changing such as research on stocks and sports news.
Developing new efficient algorithms for GAI to use
RAG as described above is an example of a new algorithm. Others in the making include Knowledge Distillation, Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN), Variational Encoders (VAEs), and Generative Diffusion Models (GDMs). The last is used for graphics and photorealistic images.
Making GPUs more efficient
AI started using Graphics Processor Units (GPUs) for machine learning because the learning and inference processes are repetitive, rather simple and require massive parallelization. But GPUs are not the ideal. Since then, nVidia has evolved their AI GPUs (Megatron-Core), and Google has come up with the Tensor Processor Unit (TPU) which is specifically designed for machine learning. Read more about GPU/TPU/NPUs here: https://www.backblaze.com/blog/ai-101-gpu-vs-tpu-vs-npu/
While ChatGPT 3 was estimated to cost US$4.6m to train, ChatGPT 5 is estimated to cost US$1.2b, with prices per transaction of training down by >33% due to improvements in hardware efficiencies.
So, while Generative AI consumes significant amounts of energy during the training and inference phases, its convenient ability to perform human level chats and ability to provide energy saving solutions offsets some of its energy disadvantages.
However, if a similar objective can be achieved by using search, please save the planet and use search instead of chatting with an LLM.
If you want to learn more about Generative AI and Sustainability, here are some courses from DreamCatcher:
AI3189 Building Custom Large Language Models (LLMs) for Generative AI (4 Days)
AI3051 Programming for Generative AI (Singapore 3-day)
2789 Application of ChatGPT in Project Implementation
1003 Machine Learning with Python
CU2554 Introduction To Sustainability/ESG (Environment, Social and Governance)






Leave A Comment